Wednesday, November 16, 2016
Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Installing Solaris 5.11 on T4-1 Blade
Installing Solaris 5.11 on T4-1 Blade
Using ILOM to connect to Server Console and Mounting ISO Image or CD/DVD
Boot sun server ok prompt
At the OK prompt type Command:: devalias
At the OK prompt type Command: boot rcdrom
Select Language
Select Installation Type
Press F2 (From Here rest of the installation screen will continue with Function F2 Key)
Select Local Disk and Press F2 to continue
In the Network configuration screen Type the Host name and select Manual Network Configuration
Enter the IP Address/SubnetMask and Default gateway
I am net configuring DNS for this server. so i am selecting Do not configure DNS
Select the Time Zone
Set Data and Time
Type ROOT user Password and you can create user on this screen
Verify the Installation Summary and press F2 to start the installation
Review the Installation Completion and Press F2 to beboot the server
Eject Installation media from ILOM
Done. Server will boot from newly installed OS
Instructions for installing the Oracle Solaris 11 operating system
Sunday, November 6, 2016
How To Access Forms Directly In Oracle Applications R12
By default in Oracle Applications R12, users are not able to access Forms directly via the following url:
http://hostname.domain:port/forms/frmservlet
The following error would pop out:
APP-FND-01542: This Applications Server is not authorized to access this database.
To allow users access to the Oracle Applications R12 directly via Forms especially in cases where access to the following url is not available:
http://hostname.domain:port/OA_HTML/AppsLogin
NOTE: Accessing Forms directly is not supported and should only be used for diagnostic and troubleshooting purposes.
Solution:
1. Edit $CONTEXT_FILE which is located in $INST_TOP/appl/admin
2. Change
SECURE
to
OFF
Application Server Security Authentication can take one of the following values {ON, OFF, SECURE}.
OFF - Server security is not checked. Any application server machine can access the database.
ON - Some level of trust is required to access the database. Either the Application Server is registered with the database or the module and version ID are known to be trusted.
SECURE - Full trust is required for access to the database. Only registered Application Server machines and trusted code modules may connect.
3. Run $INST_TOP/admin/scripts/adautocfg.sh to instantiate the changes
4. Users are now able to access Forms directly.
Reference: Doc ID 552301.1
http://hostname.domain:port/forms/frmservlet
The following error would pop out:
APP-FND-01542: This Applications Server is not authorized to access this database.
To allow users access to the Oracle Applications R12 directly via Forms especially in cases where access to the following url is not available:
http://hostname.domain:port/OA_HTML/AppsLogin
NOTE: Accessing Forms directly is not supported and should only be used for diagnostic and troubleshooting purposes.
Solution:
1. Edit $CONTEXT_FILE which is located in $INST_TOP/appl/admin
2. Change
to
Application Server Security Authentication can take one of the following values {ON, OFF, SECURE}.
OFF - Server security is not checked. Any application server machine can access the database.
ON - Some level of trust is required to access the database. Either the Application Server is registered with the database or the module and version ID are known to be trusted.
SECURE - Full trust is required for access to the database. Only registered Application Server machines and trusted code modules may connect.
3. Run $INST_TOP/admin/scripts/adautocfg.sh to instantiate the changes
4. Users are now able to access Forms directly.
Reference: Doc ID 552301.1
R12 - Logon is not working, no error message is shown
After the clone of an E-Business Suite Instance Release 12, the logon was not working as expected on the target Instance.
Launching the logon URL
http://.:
is redirected to
http://host.domain:port/OA_HTML/AppsLocalLogin.jsp
Result :
Nothing happens - no Homepage screen is presented, neither an error message is brought up.
Cause:
The cause has been identified as JSP- or Class-File corruption under the $COMMON_TOP/_pages.
The corruption could be a result of a wrong CLASSPATH Setting in the Environment, as the System itself was not able to access the Classes.
Solution:
Please execute the following steps :
1. Open a new Shell and source the APPS User Environment
2. Change into the $FND_TOP Patch directory
cd $FND_TOP/patch/115/bin
3. Compile the JSP files using following command :
perl ojspCompile.pl --compile --flush -p 2
4. Initiate the execution of Autoconfig on the DB- and the APPS_Tier(s)
5. Start the APPS-Tier(s) Services again and re-test the logon
Reference:
Doc ID 435550.1
Launching the logon URL
http://
is redirected to
http://host.domain:port/OA_HTML/AppsLocalLogin.jsp
Result :
Nothing happens - no Homepage screen is presented, neither an error message is brought up.
Cause:
The cause has been identified as JSP- or Class-File corruption under the $COMMON_TOP/_pages.
The corruption could be a result of a wrong CLASSPATH Setting in the Environment, as the System itself was not able to access the Classes.
Solution:
Please execute the following steps :
1. Open a new Shell and source the APPS User Environment
2. Change into the $FND_TOP Patch directory
cd $FND_TOP/patch/115/bin
3. Compile the JSP files using following command :
perl ojspCompile.pl --compile --flush -p 2
4. Initiate the execution of Autoconfig on the DB- and the APPS_Tier(s)
5. Start the APPS-Tier(s) Services again and re-test the logon
Reference:
Doc ID 435550.1
Thursday, October 20, 2016
Oracle SOA / BPM / Fusion Middleware Consultant
Check out this job at Tabadul: Oracle SOA / BPM / Fusion Middleware Consultant
https://www.linkedin.com/jobs2/view/197437126
Features of Oracle Identity Manager
The following are the features of Oracle Identity Manager:
-Scalable architecture
Oracle Identity Manager is based on open, standards-based technology. The J2EE application server model of Oracle Identity Manager offers scalability, failover, load-balancing, and built-in Web deployment features.
-Comprehensive user management
Oracle Identity Manager can support unlimited user organizational hierarchies and user groups with inheritance, customizable user ID policy management, password policy management, and user access policies. It also offers the feature of delegated administration with comprehensive permission settings. We can use Oracle Identity Manager to maintain resource allocation history and to manage application parameters and entitlements.
-Web-based user self-service
Oracle Identity Manager contains a user self-service portal that is customizable and Web based. This portal can be used to manage user information, change and synchronize passwords, reset passwords, request access to applications, review and edit entitlements, and work on workflow tasks.
-Flexible process engine
Using Oracle Identity Manager, we can create business and provisioning process models in applications such as Microsoft Project and Microsoft Visio. Process models include support for approval workflows and escalations. We can track the progress of each provisioning event in the workflow.
Oracle Identity Manager provides support for complex branching, self-healing processes, and nested processes with data interchange and dependencies. The process flow can be customized without making code changes.
-Comprehensive reporting for audit-trail accounting
Oracle Identity Manager provides status reports on all processes with full-state information, in real time. In addition, it even offers OLAP features.
-Automated tool for connector management
Oracle Identity Manager provides an automated tool for connector generation. This tool, which is known as the Adapter Factory, supports a wide range of interfaces, applications, and devices. The adapters generated by the Adapter Factory run on the Oracle Identity Manager server, and they do not require any agents to be installed or updated on the target systems. The use of the Adapter Factory helps speed up the process of connector development and simplifies the task of updating existing connectors.
If the target system does not have a network-enabled interface, then we can use the Oracle Identity Manager remote manager to provide an SSL-secured network communication channel and interface to local APIs that are not running on the Oracle Identity Manager server. By using the remote manager, we can run functions on target systems having APIs that are not network aware.
-Built-in change management
Oracle Identity Manager enables to package new processes, import and export existing processes, and move packages from one system to another.
-Scalable architecture
Oracle Identity Manager is based on open, standards-based technology. The J2EE application server model of Oracle Identity Manager offers scalability, failover, load-balancing, and built-in Web deployment features.
-Comprehensive user management
Oracle Identity Manager can support unlimited user organizational hierarchies and user groups with inheritance, customizable user ID policy management, password policy management, and user access policies. It also offers the feature of delegated administration with comprehensive permission settings. We can use Oracle Identity Manager to maintain resource allocation history and to manage application parameters and entitlements.
-Web-based user self-service
Oracle Identity Manager contains a user self-service portal that is customizable and Web based. This portal can be used to manage user information, change and synchronize passwords, reset passwords, request access to applications, review and edit entitlements, and work on workflow tasks.
-Flexible process engine
Using Oracle Identity Manager, we can create business and provisioning process models in applications such as Microsoft Project and Microsoft Visio. Process models include support for approval workflows and escalations. We can track the progress of each provisioning event in the workflow.
Oracle Identity Manager provides support for complex branching, self-healing processes, and nested processes with data interchange and dependencies. The process flow can be customized without making code changes.
-Comprehensive reporting for audit-trail accounting
Oracle Identity Manager provides status reports on all processes with full-state information, in real time. In addition, it even offers OLAP features.
-Automated tool for connector management
Oracle Identity Manager provides an automated tool for connector generation. This tool, which is known as the Adapter Factory, supports a wide range of interfaces, applications, and devices. The adapters generated by the Adapter Factory run on the Oracle Identity Manager server, and they do not require any agents to be installed or updated on the target systems. The use of the Adapter Factory helps speed up the process of connector development and simplifies the task of updating existing connectors.
If the target system does not have a network-enabled interface, then we can use the Oracle Identity Manager remote manager to provide an SSL-secured network communication channel and interface to local APIs that are not running on the Oracle Identity Manager server. By using the remote manager, we can run functions on target systems having APIs that are not network aware.
-Built-in change management
Oracle Identity Manager enables to package new processes, import and export existing processes, and move packages from one system to another.
Deployment Configurations of Oracle Identity Manager
Following are the deployment configurations of Oracle Identity Manager
Provisioning
We can use Oracle Identity Manager to create, maintain, and delete accounts on target systems. Oracle Identity Manager becomes the front-end entry point for managing all the accounts on these systems. After the accounts are provisioned, the users for whom accounts have been provisioned are able to access the target systems without any interaction with Oracle Identity Manager. This is the provisioning configuration of Oracle Identity Manager.
The purpose of provisioning is to automate the creation and maintenance of user accounts on target systems. Provisioning is also used to accommodate any requirement for workflow approvals and auditing that may be a component of that provisioning lifecycle.
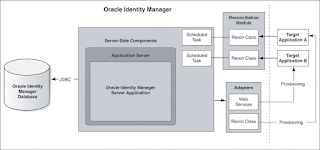
Provisioning Configuration of Oracle Identity Manager
Provisioning events are initiated either through requests or by direct provisioning.
A request can be manually created by an administrator or, in certain cases, by target users themselves. Oracle Identity Manager automatically creates requests for some events. For example, a request is automatically created when Oracle Identity Manager enforces the requirements of an access policy. We can also use Oracle Identity Manager to create approval processes that can be run as part of the request-based provisioning cycle.
Direct provisioning is a special administrator-only function for creating an account for a particular user on a target application without having to wait for any workflow or approval processes.
Reconciliation
Oracle Identity Manager provides a centralized control mechanism to manage user accounts and entitlements and to control user access to resources. However, we can choose not to use Oracle Identity Manager as the primary repository or the front-end entry point of user accounts. Instead, we can use Oracle Identity Manager to periodically poll your system applications to maintain an accurate profile of all accounts that exist on those systems. This is the reconciliation configuration of Oracle Identity Manager.
Reconciliation Configuration of Oracle Identity Manager
Oracle Identity Manager is used only as an archive for all account management actions that are performed on the target system. It is assumed that user accounts are created, deleted, and maintained by the local resource-specific administrators.
Reconciliation involves using the user discovery and account discovery features of Oracle Identity Manager.
User discovery is the process of recognizing the existence of a user account on a primary database. The primary database is the repository that is considered to contain the master list of user accounts. Within the context of user discovery and reconciliation, the primary database is also referred to as the trusted source or authoritative source. There may be more than one trusted source for each Oracle Identity Manager environment.
Account discovery is the process of recognizing changes to user-related information on resources. If the information that is changed affects the user's primary record, it is generally a change associated with a trusted source. If the information that is changed is related to a user's access to a resource, it is generally a change associated with a target resource.
Different forms of reconciliation:
One-Time Reconciliation
We can use Oracle Identity Manager to perform a single, one-time reconciliation with a legacy target system. The purpose of this form of reconciliation is to import all accounts on that system into Oracle Identity Manager. After one-time reconciliation is performed, we can use Oracle Identity Manager to provision accounts for your users.
Target Resource Reconciliation
Trusted Source Reconciliation
Provisioning and Reconciliation
Provisioning and reconciliation configuration in which we can use Oracle Identity Manager to perform both provisioning and reconciliation tasks. In this configuration, it is assumed that allow accounts on target systems to be created and maintained by both local administrators and Oracle Identity Manager.
To achieve this configuration, one must perform all the steps associated with setting up both provisioning and reconciliation.
Provisioning
We can use Oracle Identity Manager to create, maintain, and delete accounts on target systems. Oracle Identity Manager becomes the front-end entry point for managing all the accounts on these systems. After the accounts are provisioned, the users for whom accounts have been provisioned are able to access the target systems without any interaction with Oracle Identity Manager. This is the provisioning configuration of Oracle Identity Manager.
The purpose of provisioning is to automate the creation and maintenance of user accounts on target systems. Provisioning is also used to accommodate any requirement for workflow approvals and auditing that may be a component of that provisioning lifecycle.
Provisioning Configuration of Oracle Identity Manager
Provisioning events are initiated either through requests or by direct provisioning.
A request can be manually created by an administrator or, in certain cases, by target users themselves. Oracle Identity Manager automatically creates requests for some events. For example, a request is automatically created when Oracle Identity Manager enforces the requirements of an access policy. We can also use Oracle Identity Manager to create approval processes that can be run as part of the request-based provisioning cycle.
Direct provisioning is a special administrator-only function for creating an account for a particular user on a target application without having to wait for any workflow or approval processes.
Reconciliation
Oracle Identity Manager provides a centralized control mechanism to manage user accounts and entitlements and to control user access to resources. However, we can choose not to use Oracle Identity Manager as the primary repository or the front-end entry point of user accounts. Instead, we can use Oracle Identity Manager to periodically poll your system applications to maintain an accurate profile of all accounts that exist on those systems. This is the reconciliation configuration of Oracle Identity Manager.
Reconciliation Configuration of Oracle Identity Manager
Oracle Identity Manager is used only as an archive for all account management actions that are performed on the target system. It is assumed that user accounts are created, deleted, and maintained by the local resource-specific administrators.
Reconciliation involves using the user discovery and account discovery features of Oracle Identity Manager.
User discovery is the process of recognizing the existence of a user account on a primary database. The primary database is the repository that is considered to contain the master list of user accounts. Within the context of user discovery and reconciliation, the primary database is also referred to as the trusted source or authoritative source. There may be more than one trusted source for each Oracle Identity Manager environment.
Account discovery is the process of recognizing changes to user-related information on resources. If the information that is changed affects the user's primary record, it is generally a change associated with a trusted source. If the information that is changed is related to a user's access to a resource, it is generally a change associated with a target resource.
Different forms of reconciliation:
One-Time Reconciliation
We can use Oracle Identity Manager to perform a single, one-time reconciliation with a legacy target system. The purpose of this form of reconciliation is to import all accounts on that system into Oracle Identity Manager. After one-time reconciliation is performed, we can use Oracle Identity Manager to provision accounts for your users.
Target Resource Reconciliation
Trusted Source Reconciliation
Provisioning and Reconciliation
Provisioning and reconciliation configuration in which we can use Oracle Identity Manager to perform both provisioning and reconciliation tasks. In this configuration, it is assumed that allow accounts on target systems to be created and maintained by both local administrators and Oracle Identity Manager.
To achieve this configuration, one must perform all the steps associated with setting up both provisioning and reconciliation.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Some Tips About FNDLOAD
Data Synchronization Data Synchronization is a process in which some setup data would be synchronized, and this would be more important w...
-
How to customize Java Virtual Machine Settings in Oracle WebLogic Server To achieve the best performance of the application and avoid perfor...
-
Identify Memory Requirement. Following queries show you how to display the relevant memory information and how to combine with a single stat...
-
Part 1 Introduction to Installing Oracle Fusion Applications 1.1 Certification 1.2 Obtain Oracle Fusion Applications Software Media Downlo...