Oracle Identity Manager automates access rights management, security, and provisioning of IT resources. This chapter provides an overview of Oracle Identity Manager.
Architecture of Oracle Identity Manager
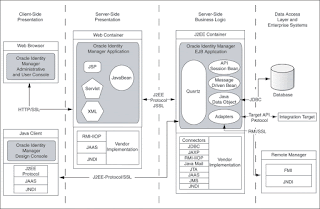
Oracle Identity Manager is based on the n-tier J2EE application architecture.
Tiers of the Oracle Identity Manager architecture:
Presentation Layer
The Presentation layer consists of two clients: the Oracle Identity Manager Administrative and User Console and the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console. The Administrative and User Console is a Web-based thin client that can be accessed from any Web browser. This console provides user self-service and delegated administration features that serve most of the provisioning requirements.
The Design Console provides the full range of the Oracle Identity Manager system configuration and development capabilities including Form Designer, Workflow Designer, and the Adapter Factory. You can access the Design Console by using a desktop Java client.
Dynamic Presentation Logic Layer
Because both the Administrative and User Console and the Design Console are highly dynamic, the Dynamic Presentation Logic layer guides the content displayed on these interfaces. In the case of the Administrative and User Console, there is a clear separation between the Presentation and Presentation Logic Layer. No such boundary exists in the Design Console.
Business Logic Layer
The Business Logic layer is implemented as an EJB application. Oracle Identity Manager runs on leading J2EE-compliant application server platforms, leveraging the J2EE services provided by these application servers to deliver a high-performance, fault-tolerant enterprise application.
The following are components of the Business Logic layer:
Application Server
The application server on which Oracle Identity Manager runs provides life-cycle management, security, deployment, and run-time services to the logical components that make up Oracle Identity Manager. These services include:
-Scalable management of resources (clustering and failover)
-Transaction management
-Security management
-Client access
-Technology resources (such as database connection pooling and messaging)
Client Interfaces and Business Logic Implementation
The core functionality of the Oracle Identity Manager platform is implemented in Java using a highly modular, object-oriented methodology. This includes the various engines that comprise the Oracle Identity Manager platform: Workflow Engine, Request Engine, User Management Engine, Rule Engine, and Reconciliation Engine. It also includes the integration layer based on the Adapter Factory, which dynamically generates integration code based on the metadata definition of the adapters.
Access to the functionality of the platform is through a set of EJB Beans. These session beans can be divided into two types:
-Nonpublished APIs: These are session beans that expose functionality used only by the Design Console.
-Published Public APIs: These are session beans that expose the public functionality of Oracle Identity Manager.
The API layer provides access to high-level functionality in Oracle Identity Manager. It is the basis for the functionality implemented in the Oracle Identity Manager Administrative and User Console. It is also the interface that custom clients can use to access Oracle Identity Manager functionality.
Data Access Layer
J2EE contains several technologies for manipulating and interacting with transactional resources (such as databases) that are based on JDBC, JTA, and JTS. The Oracle Identity Manager architecture leverages the following J2EE services:
-Database connection pooling
-Integration with JNDI (lookup of DataSources in the JNDI namespace)
-XA compliance
-Batch updates
The system administrator can manage data sources in the same manner in which all standard J2EE applications in the enterprise are managed. Oracle Identity Manager can use these data sources to communicate with the database tier.
Backend System Integration Layer
The Backend System Integration layer can be divided into the following:
-Database
-Remote Manager
Database
The Database tier consists of the Oracle Identity Manager repository, which manages and stores Oracle Identity Manager metadata in an ANSI SQL 92-compliant relational database. All the data resides in the Oracle Identity Manager repository.
Remote Manager
The remote manager is an Oracle Identity Manager server component that runs on a target system computer. It provides the network and security layer required to integrate with applications that do not have network-aware APIs or do not provide security. It is built as a lightweight RMI server. The communication protocol is RMI tunneled over HTTP/S.
The J2EE RMI framework enables the creation of virtually transparent, distributed services and applications. RMI-based applications consist of Java objects making method calls to one another, regardless of their location. This enables one Java object to call methods on another Java object residing on another virtual computer in the same manner in which methods are called on a Java object residing on the same virtual computer.
Thursday, October 20, 2016
How to install patches or updates for your VMware ESX host using update manager
How to install patches or updates for your VMware ESX host using update manager
1. Download patches and upgrades
Begin by logging onto the vSphere client. From the vSphere client home screen click on the “Update Manager” icon.
From the Update Manager Administration window select the “Admin View” tab.
Select the “Getting Started” tab. and Click on Download patches and upgrades.
Make sure the vSphere server has access to internet to download the required patches and updates from VMware repository.
2. Create a Baseline Group.
To create baselines go to the Update Manager home screen select the “Baselines and Groups” tab, from the “Baseline” section on the left click the "Create" link:
Enter Baseline Group name
Click next
Click next
Select Baselines for this group.
Select the required options and click next
1. Critical Host Patches (Predefined)
Checks ESX/ESXi hosts for compliance with all critical patches
2. Non-Critical Host Patches (Predefined)
Checks ESX/ESXi hosts for compliance with all optional patches.
Click next
Click Finish
1. Download patches and upgrades
Begin by logging onto the vSphere client. From the vSphere client home screen click on the “Update Manager” icon.
From the Update Manager Administration window select the “Admin View” tab.
Select the “Getting Started” tab. and Click on Download patches and upgrades.
Make sure the vSphere server has access to internet to download the required patches and updates from VMware repository.
2. Create a Baseline Group.
To create baselines go to the Update Manager home screen select the “Baselines and Groups” tab, from the “Baseline” section on the left click the "Create" link:
Enter Baseline Group name
Click next
Click next
Select Baselines for this group.
Select the required options and click next
1. Critical Host Patches (Predefined)
Checks ESX/ESXi hosts for compliance with all critical patches
2. Non-Critical Host Patches (Predefined)
Checks ESX/ESXi hosts for compliance with all optional patches.
Click next
Click Finish
How to boot a VM into Safe Mode in ESXi
1) Right Click the VM
2) Select Edit Settings
a. Click Options
b. Select Boot Options
c. Set the Power-on Boot Delay to 5000ms (5 seconds)
d. Now the VM will display the BIOS VMWare bios screen for 5 seconds, giving you enough time to click the VM and press F8
3) Open the console window for the VM. Start the boot process.
4) Click the console with the mouse to gain focus.
5) Wait until the VMWare boot screen appears.
6) Before the counter reaches 0:00 press the F8 key and don't let up until the Windows Advanced Options Menu appears which will allow selecting the Safe Mode or other options.
2) Select Edit Settings
a. Click Options
b. Select Boot Options
c. Set the Power-on Boot Delay to 5000ms (5 seconds)
d. Now the VM will display the BIOS VMWare bios screen for 5 seconds, giving you enough time to click the VM and press F8
3) Open the console window for the VM. Start the boot process.
4) Click the console with the mouse to gain focus.
5) Wait until the VMWare boot screen appears.
6) Before the counter reaches 0:00 press the F8 key and don't let up until the Windows Advanced Options Menu appears which will allow selecting the Safe Mode or other options.
Thursday, August 4, 2016
How to change User Name or Login name of Oracle EBS users
How to change User Name or Login name of Oracle EBS users
If you want to implement Single Sign On (SSO) Or you need to standardize username to match oracle username with Active Directory usernames, oracle provided a simple API to accomplish this task. However it works fine when done from ERP Application front end but to update all the user names is a tedious job or we can use some tools like data loader to change the usernames from the front end.
Using APPS.FND_USER_PKG API to change the username as well as update the related WF tables.
1. Collect the list of users
Identify the active users from fnd_user excluding seeded users.
SQL> SELECT user_name
FROM fnd_user
WHERE end_date IS NOT NULL
AND user_name NOT IN
('SYSADMIN',
'AUTOINSTALL',
'GUEST',
'IEXADMIN',
'OP_SYSADMIN',
'ASGUEST',
'IRC_EXT_GUEST',
'IRC_EMP_GUEST',
'PORTAL30',
'PORTAL30_SSO',
'XML_USER');
2. Modify the user name
Execute the below procedure to change the user name.
SQL> BEGIN
fnd_user_pkg.change_user_name (x_old_user_name => 'OLDUSERNAME',
x_new_user_name => 'NEWUSERNAME'
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
3. Update WF_NOTIFICATIONS.receipient_role with new user names.
After changing the username, users cannot find their old notifications in the worklist.
Execute the below procedure to update the user name.
SQL> exec WF_MAINTENANCE.PropagateChangedName('OLDUSERNAME','NEWUSERNAME');
(4) Execute the following query to find out if the usernames in WF_NOTIFICATIONS were changed
SQL> select notification_id, begin_date, end_date, mail_status, status,recipient_role
from wf_notifications
where recipient_role in ('OLDUSERNAME');
Above query should not supposed to return any rows for old user names.
5. Verify the change
SQL> select user_name, end_date from fnd_user where user_name='NEWUSERNAME';
USER_NAME |END_DATE
------------------|---------
NEWUSERNAME |
SQL> select user_name, role_name from wf_local_user_roles where user_name='NEWUSERNAME';
USER_NAME |ROLE_NAME
-----------------------|-------------------------------------
NEWUSERNAME |FND_RESP|SQLGL|MS_GL|STANDARD
NEWUSERNAME |FND_RESP|SYSADMIN|SYSTECH|STANDARD
NEWUSERNAME |FND_RESP|SYSADMIN|SYSTEM_ADMINISTRATOR|STANDARD
The new user name is being accepted at login. Checked few old transactions created by the user for verification.
If you want to implement Single Sign On (SSO) Or you need to standardize username to match oracle username with Active Directory usernames, oracle provided a simple API to accomplish this task. However it works fine when done from ERP Application front end but to update all the user names is a tedious job or we can use some tools like data loader to change the usernames from the front end.
Using APPS.FND_USER_PKG API to change the username as well as update the related WF tables.
1. Collect the list of users
Identify the active users from fnd_user excluding seeded users.
SQL> SELECT user_name
FROM fnd_user
WHERE end_date IS NOT NULL
AND user_name NOT IN
('SYSADMIN',
'AUTOINSTALL',
'GUEST',
'IEXADMIN',
'OP_SYSADMIN',
'ASGUEST',
'IRC_EXT_GUEST',
'IRC_EMP_GUEST',
'PORTAL30',
'PORTAL30_SSO',
'XML_USER');
2. Modify the user name
Execute the below procedure to change the user name.
SQL> BEGIN
fnd_user_pkg.change_user_name (x_old_user_name => 'OLDUSERNAME',
x_new_user_name => 'NEWUSERNAME'
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
3. Update WF_NOTIFICATIONS.receipient_role with new user names.
After changing the username, users cannot find their old notifications in the worklist.
Execute the below procedure to update the user name.
SQL> exec WF_MAINTENANCE.PropagateChangedName('OLDUSERNAME','NEWUSERNAME');
(4) Execute the following query to find out if the usernames in WF_NOTIFICATIONS were changed
SQL> select notification_id, begin_date, end_date, mail_status, status,recipient_role
from wf_notifications
where recipient_role in ('OLDUSERNAME');
Above query should not supposed to return any rows for old user names.
5. Verify the change
SQL> select user_name, end_date from fnd_user where user_name='NEWUSERNAME';
USER_NAME |END_DATE
------------------|---------
NEWUSERNAME |
SQL> select user_name, role_name from wf_local_user_roles where user_name='NEWUSERNAME';
USER_NAME |ROLE_NAME
-----------------------|-------------------------------------
NEWUSERNAME |FND_RESP|SQLGL|MS_GL|STANDARD
NEWUSERNAME |FND_RESP|SYSADMIN|SYSTECH|STANDARD
NEWUSERNAME |FND_RESP|SYSADMIN|SYSTEM_ADMINISTRATOR|STANDARD
The new user name is being accepted at login. Checked few old transactions created by the user for verification.
Wednesday, January 14, 2015
How to Allow in R12 to Open Multiple Forms in the Same Session
How to open multiple forms with the same responsibility in the same session for Release 12.
Under 'Tools' menu, uncheck the Close Other Forms option to allow multiple Forms windows in one Forms session. Navigate to Tools->Close Other Forms.
Under 'Tools' menu, uncheck the Close Other Forms option to allow multiple Forms windows in one Forms session. Navigate to Tools->Close Other Forms.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Some Tips About FNDLOAD
Data Synchronization Data Synchronization is a process in which some setup data would be synchronized, and this would be more important w...
-
How to customize Java Virtual Machine Settings in Oracle WebLogic Server To achieve the best performance of the application and avoid perfor...
-
Identify Memory Requirement. Following queries show you how to display the relevant memory information and how to combine with a single stat...
-
Part 1 Introduction to Installing Oracle Fusion Applications 1.1 Certification 1.2 Obtain Oracle Fusion Applications Software Media Downlo...